Make no mistake, this was Australia’s Brexit.
 <heartbroken rant>
<heartbroken rant>
Seeing the referendum to give a Voice to Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples profoundly defeated across Australia today is heart-breaking and confusing.
My heart goes out to all Australians feeling let down, but especially, of course, to the Indigenous people of this country for whom this would have been, at least, one small step in the right direction.
As someone who researches online communication, digital platforms and how we communicate and tell stories to each other, I fear the impact of this referendum will be even wider still.
The rampant and unabashed misinformation and disinformation that washed over social media, and was then amplified and normalised as it was reported in mainstream media, is more than worrying.
Make no mistake, this was Australia’s Brexit. It was the pilot, the test, to see how far disinformation can succeed in campaigning in this country. And succeed it did.
In the UK, the pretty devastating economic impact of Brexit has revealed the lies that drove campaigning for it (as have former campaigners who admitted the truth was no barrier for them).
I fear most non-Indigenous Australians will not have as clear and unambiguous a sign that they’ve been lied to, at least this time.
In Australia, the mechanisms of disinformation have now been tested, polished, refined and sharpened. They will be a force to be reckoned with in all coming elections. And our electoral laws lack the teeth to do almost anything about that right now.
I do not believe that today’s result is just down to disinformation, but I do believe it played a significant role. I’m not sure if it changed the outcome, but I’m not sure it didn’t, either.
There was research that warned about the unprecedented levels of misinformation looking at early campaigning around the Voice. There will be more that looks back after this result.
But before another election comes along, we need more than just research. We need more than just improved digital literacies, although that’s profoundly necessary.
We need critical thinking like never before, we need to equip people to make informed choices by being able to spot bullshit in its myriad forms.
I am under no illusion that means people will agree, but they deserve to have tools to make an actually informed choice. Not a coerced one. Social media isn’t just entertainment; it’s our political sphere. Messages don’t just live on social media, even if they start there.
Messages might start digital, but they travel across all media, old and new.
I know this is a rant after a profoundly disappointing referendum, and probably not the best expressed one. But there is so much work to do if this country isn’t even more assailed by weaponised disinformation at every turn.
</heartbroken rant>
The Future of Twitter (Podcast)
I was pleased to join Sarah Tallier and The Future Of team to discuss how Twitter has changed since being purchased by Elon Musk, what this means for Twitter as some form of public sphere, and what alternatives are emerging (Mastodon!).
We discuss:
Will Twitter ever be the same since Elon Musk’s takeover? And what impact will his changes have on users, free speech and (dis)information?
Twitter is one of the most influential speech platforms in the world – as of 2022, it had approximately 450million monthly active users. But its takeover by Elon Musk has sparked concerns about social media regulation and Twitter’s ability to remain a ‘proxy for public opinion’.
To explore this topic, Sarah is joined by Tama Leaver, Professor of Internet Studies at Curtin University.
- Why does Twitter matter? [00:48]
- Elon rewinds content regulation [06:54]
- Twitter’s political clout [10:16]
- Make the internet democratic again [11:28]
- What is Mastodon? [15:29]
- Can we ever really trust the internet? [17:47]
And there’s a transcript here.
Banning ChatGPT in Schools Hurts Our Kids
![Learning with Technology [Image: “Learning with technology” generated by Lexica, 1 February 2023]](https://www.tamaleaver.net/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/0fa4f0c3-f56a-41fb-b04a-a962eeb666f4.jpg) As new technologies emerge, educators have an opportunity to help students think about the best practical and ethical uses of these tools, or hide their heads in the sand and hope it’ll be someone else’s problem.
As new technologies emerge, educators have an opportunity to help students think about the best practical and ethical uses of these tools, or hide their heads in the sand and hope it’ll be someone else’s problem.
It’s incredibly disappointing to see the Western Australian Department of Education forcing every state teacher to join the heads in the sand camp, banning ChatGPT in state schools.
Generative AI is here to stay. By the time they graduate, our kids will be in jobs where these will be important creative and productive tools in the workplace and in creative spaces.
Education should be arming our kids with the critical skills to use, evaluate and extend the uses and outputs of generative AI in an ethical way. Not be forced to try them out behind closed doors at home because our education system is paranoid that every student will somehow want to use these to cheat.
For many students, using these tools to cheat probably never occurred to them until they saw headlines about it in the wake of WA joining a number of other states in this reactionary ban.
Young people deserve to be part of the conversation about generative AI tools, and to help think about and design the best practical and ethical uses for the future.
Schools should be places where those conversations can flourish. Having access to the early versions of tomorrow’s tools today is vital to helping those conversations start.
Sure, getting around a school firewall takes one kid with a smartphone using it as a hotspot, or simply using a VPN. But they shouldn’t need to resort to that. Nor should students from more affluent backgrounds be more able to circumvent these bans than others.
Digital and technological literacies are part of the literacy every young person will need to flourish tomorrow. Education should be the bastion equipping young people for the world they’re going to be living in. Not trying to prevent them thinking about it at all.
[Image: “Learning with technology” generated by Lexica, 1 February 2023]
Update: Here’s an audio file of an AI speech synthesis tool by Eleven Labs reading this blog post:
Watching Musk fiddle while Twitter burns
Seeing Elon Musk pledge to reinstate Trump on Twitter understandably starts another wave of folks leaving the platform, but if we all leave Twitter, won’t it just become what Trump dreamed Parler would be?
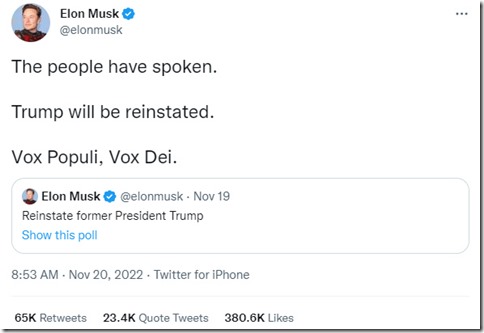
I’ve been on Twitter for more than 15 years, and it’s the platform that has most felt like home for the majority of that time. I’m heartbroken by what Musk has managed to do to the platform and the people who (mostly used to, now) run it in a few short weeks. His flagrant disregard for users or the platform itself is gutting. (I’m with Nancy Baym on what’s being lost here, even if the platform stays online and doesn’t fall over.)
For better or worse, the media broadly (and academia in many ways, to be fair) has used Twitter as a proxy of public opinion. That won’t change overnight. If mostly moderate and left-leaning voices leave, does that give Trump via Musk exactly what he always wanted?
Trump gets Twitter as a pulpit to say whatever half-formed thought escapes his head, and a crowd of MAGA voices to cheer him on at every step. While the echo chamber idea has been widely challenged, it feels like this could be how that chamber would actually cohere.
From outside the US, that anyone, let alone a meaningful percentage, of US citizens believe the Biden election was ‘stolen’ feels like it shows exactly how powerful and destructive the Trump’s Twitter can be.
I don’t want to be putting dollars in Musk’s pocket either as he burns users and employees alike, but I’m deeply conflicted about just leaving the space which still has 15 years of ‘public square’ reputation. I don’t have a solution, but I have many fears.
And, yes, like many I’ve set up on Mastodon to see how that space evolves.
Spotlight forum: social media, child influencers and keeping your kids safe online

I was pleased to join Associate Professor Crystal Abidin as panellists on the ABC Perth Radio Spotlight Forum on social media, child influencers and keeping your kids safe online. It was a wide-ranging discussion that really highlights community interest and concern in ensuring our young people have the best access to opportunities online while minimising the risks involved.
You can listen to a recording of the broadcast here.
Coroner finds social media contributed to 14-year-old Molly Russell’s death. How should parents and platforms react?
Last week, London coroner Andrew Walker delivered his findings from the inquest into 14-year-old schoolgirl Molly Russell’s death, concluding she “died from an act of self harm while suffering from depression and the negative effects of online content”.
The inquest heard Molly had used social media, specifically Instagram and Pinterest, to view large amounts of graphic content related to self-harm, depression and suicide in the lead-up to her death in November 2017.
The findings are a damning indictment of the big social media platforms. What should they be doing in response? And how should parents react in light of these events?
Social media use carries risk
The social media landscape of 2022 is different to the one Molly experienced in 2017. Indeed, the initial public outcry after her death saw many changes to Instagram and other platforms to try and reduce material that glorifies depression or self-harm.
Instagram, for example, banned graphic self-harm images, made it harder to search for non-graphic self-harm material, and started providing information about getting help when users made certain searches.
BBC journalist Tony Smith noted that the press team for Instagram’s parent company Meta requested that journalists make clear these sorts of images are no longer hosted on its platforms. Yet Smith found some of this content was still readily accessible today.
Also, in recent years Instagram has been found to host pro-anorexia accounts and content encouraging eating disorders. So although platforms may have made some positive changes over time, risks still remain.
That said, banning social media content is not necessarily the best approach.
What can parents do?
Here are some ways parents can address concerns about their children’s social media use.
Open a door for conversation, and keep it open
It’s not always easy to get young people to open up about what they’re feeling, but it’s clearly important to make it as easy and safe as possible for them to do so.
Research has shown creating a non-judgemental space for young people to talk about how social media makes them feel will encourage them to reach out if they need help. Also, parents and young people can often learn from each other through talking about their online experiences.
Try not to overreact
Social media can be an important, positive and healthy part of a young person’s life. It is where their peers and social groups are found, and during lockdowns was the only way many young people could support and talk to each other.
Completely banning social media may prevent young people from being a part of their peer groups, and could easily do more harm than good.
Negotiate boundaries together
Parents and young people can agree on reasonable rules for device and social media use. And such agreements can be very powerful.
They also present opportunities for parents and carers to model positive behaviours. For example, both parties might reach an agreement to not bring their devices to the dinner table, and focus on having conversations instead.
Another agreement might be to charge devices in a different room overnight so they can’t be used during normal sleep times.
What should social media platforms do?
Social media platforms have long faced a crisis of trust and credibility. Coroner Walker’s findings tarnish their reputation even further.
Now’s the time for platforms to acknowledge the risks present in the service they provide and make meaningful changes. That includes accepting regulation by governments.
More meaningful content moderation is needed
During the pandemic, more and more content moderation was automated. Automated systems are great when things are black and white, which is why they’re great at spotting extreme violence or nudity. But self-harm material is often harder to classify, harder to moderate and often depends on the context it’s viewed in.
For instance, a picture of a young person looking at the night sky, captioned “I just want to be one with the stars”, is innocuous in many contexts and likely wouldn’t be picked up by algorithmic moderation. But it could flag an interest in self-harm if it’s part of a wider pattern of viewing.
Human moderators do a better job determining this context, but this also depends on how they’re resourced and supported. As social media scholar Sarah Roberts writes in her book Behind the Screen, content moderators for big platforms often work in terrible conditions, viewing many pieces of troubling content per minute, and are often traumatised themselves.
If platforms want to prevent young people seeing harmful content, they’ll need to employ better-trained, better-supported and better-paid moderators.
Harm prevention should not be an afterthought
Following the inquest findings, the new Prince and Princess of Wales astutely tweeted “online safety for our children and young people needs to be a prerequisite, not an afterthought”.
For too long, platforms have raced to get more users, and have only dealt with harms once negative press attention became unavoidable. They have been left to self-regulate for too long.
The foundation set up by Molly’s family is pushing hard for the UK’s Online Safety Bill to be accepted into law. This bill seeks to reduce the harmful content young people see, and make platforms more accountable for protecting them from certain harms. It’s a start, but there’s already more that could be done.
In Australia the eSafety Commissioner has pushed for Safety by Design, which aims to have protections built into platforms from the ground up.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14.![]()
Tama Leaver, Professor of Internet Studies, Curtin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
ABC Perth Spotlight forum: how to protect your privacy in an increasingly tech-driven world
 I was pleased to be part of the ABC Perth Radio’s Spotlight Forum on ‘How to Protect Your Privacy in an Increasingly Tech-driven World‘ this morning, hosted by Nadia Mitsopoulos, and also featuring Associate Professor Julia Powles, Kathryn Gledhill-Tucker from Electronic Frontiers Australia and David Yates from Corrs Chambers Westgarth.
I was pleased to be part of the ABC Perth Radio’s Spotlight Forum on ‘How to Protect Your Privacy in an Increasingly Tech-driven World‘ this morning, hosted by Nadia Mitsopoulos, and also featuring Associate Professor Julia Powles, Kathryn Gledhill-Tucker from Electronic Frontiers Australia and David Yates from Corrs Chambers Westgarth.
You can stream the Forum on the ABC website, or download here.

Instagram’s privacy updates for kids are positive. But plans for an under-13s app means profits still take precedence

Shutterstock
By Tama Leaver, Curtin University
Facebook recently announced significant changes to Instagram for users aged under 16. New accounts will be private by default, and advertisers will be limited in how they can reach young people.
The new changes are long overdue and welcome. But Facebook’s commitment to childrens’ safety is still in question as it continues to develop a separate version of Instagram for kids aged under 13.
The company received significant backlash after the initial announcement in May. In fact, more than 40 US Attorneys General who usually support big tech banded together to ask Facebook to stop building the under-13s version of Instagram, citing privacy and health concerns.
Privacy and advertising
Online default settings matter. They set expectations for how we should behave online, and many of us will never shift away from this by changing our default settings.
Adult accounts on Instagram are public by default. Facebook’s shift to making under-16 accounts private by default means these users will need to actively change their settings if they want a public profile. Existing under-16 users with public accounts will also get a prompt asking if they want to make their account private.
These changes normalise privacy and will encourage young users to focus their interactions more on their circles of friends and followers they approve. Such a change could go a long way in helping young people navigate online privacy.
Facebook has also limited the ways in which advertisers can target Instagram users under age 18 (or older in some countries). Instead of targeting specific users based on their interests gleaned via data collection, advertisers can now only broadly reach young people by focusing ads in terms of age, gender and location.
This change follows recently publicised research that showed Facebook was allowing advertisers to target young users with risky interests — such as smoking, vaping, alcohol, gambling and extreme weight loss — with age-inappropriate ads.
This is particularly worrying, given Facebook’s admission there is “no foolproof way to stop people from misrepresenting their age” when joining Instagram or Facebook. The apps ask for date of birth during sign-up, but have no way of verifying responses. Any child who knows basic arithmetic can work out how to bypass this gateway.
Of course, Facebook’s new changes do not stop Facebook itself from collecting young users’ data. And when an Instagram user becomes a legal adult, all of their data collected up to that point will then likely inform an incredibly detailed profile which will be available to facilitate Facebook’s main business model: extremely targeted advertising.
Deploying Instagram’s top dad
Facebook has been highly strategic in how it released news of its recent changes for young Instagram users. In contrast with Facebook’s chief executive Mark Zuckerberg, Instagram’s head Adam Mosseri has turned his status as a parent into a significant element of his public persona.
Since Mosseri took over after Instagram’s creators left Facebook in 2018, his profile has consistently emphasised he has three young sons, his curated Instagram stories include #dadlife and Lego, and he often signs off Q&A sessions on Instagram by mentioning he needs to spend time with his kids.
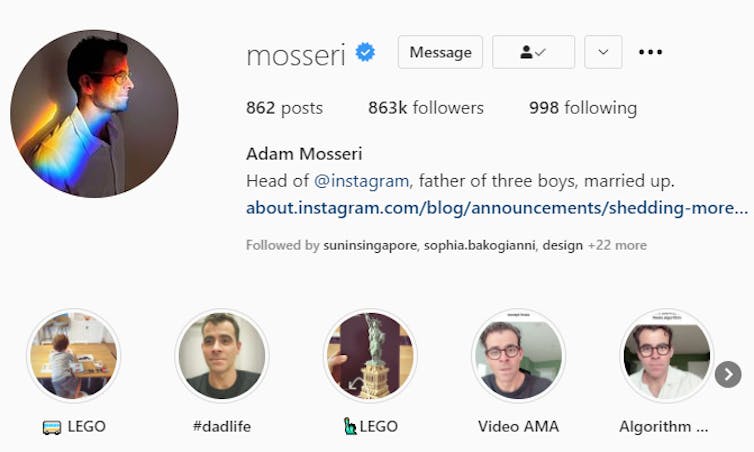
When Mosseri posted about the changes for under-16 Instagram users, he carefully framed the news as coming from a parent first, and the head of one of the world’s largest social platforms second. Similar to many influencers, Mosseri knows how to position himself as relatable and authentic.
Age verification and ‘potentially suspicious’ adults
In a paired announcement on July 27, Facebook’s vice-president of youth products Pavni Diwanji announced Facebook and Instagram would be doing more to ensure under-13s could not access the services.
Diwanji said Facebook was using artificial intelligence algorithms to stop “adults that have shown potentially suspicious behavior” from being able to view posts from young people’s accounts, or the accounts themselves. But Facebook has not offered an explanation as to how a user might be found to be “suspicious”.
Diwanji notes the company is “building similar technology to find and remove accounts belonging to people under the age of 13”. But this technology isn’t being used yet.
It’s reasonable to infer Facebook probably won’t actively remove under-13s from either Instagram or Facebook until the new Instagram For Kids app is launched — ensuring those young customers aren’t lost to Facebook altogether.
Despite public backlash, Diwanji’s post confirmed Facebook is indeed still building “a new Instagram experience for tweens”. As I’ve argued in the past, an Instagram for Kids — much like Facebook’s Messenger for Kids before it — would be less about providing a gated playground for children and more about getting children familiar and comfortable with Facebook’s family of apps, in the hope they’ll stay on them for life.
A Facebook spokesperson told The Conversation that a feature introduced in March prevents users registered as adults from sending direct messages to users registered as teens who are not following them.
“This feature relies on our work to predict peoples’ ages using machine learning technology, and the age people give us when they sign up,” the spokesperson said.
They said “suspicious accounts will no longer see young people in ‘Accounts Suggested for You’, and if they do find their profiles by searching for them directly, they won’t be able to follow them”.
Resources for parents and teens
For parents and teen Instagram users, the recent changes to the platform are a useful prompt to begin or to revisit conversations about privacy and safety on social media.
Instagram does provide some useful resources for parents to help guide these conversations, including a bespoke Australian version of their Parent’s Guide to Instagram created in partnership with ReachOut. There are many other online resources, too, such as CommonSense Media’s Parents’ Ultimate Guide to Instagram.
Regarding Instagram for Kids, a Facebook spokesperson told The Conversation the company hoped to “create something that’s really fun and educational, with family friendly safety features”.
But the fact that this app is still planned means Facebook can’t accept the most straightforward way of keeping young children safe: keeping them off Facebook and Instagram altogether.
![]()
Tama Leaver, Professor of Internet Studies, Curtin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.