Home » Posts tagged 'web presence'
Tag Archives: web presence
Strategies for Developing a Scholarly Web Presence During a Higher Degree
As part of the Curtin Humanities Research Skills and Careers Workshops 2015 I recently facilitated a workshop entitled Strategies for Developing a Scholarly Web Presence During a Higher Degree. As the workshop received a very positive response and addressed a number of strategies and issues that participants had not addressed previously, I thought I’d share the slides here in case they’re of use to others.
For more context regarding scholarly use of social media in particular, it’s worth checking out Deborah Lupton’s 2014 report ‘Feeling Better Connected’: Academics’ Use of Social Media.
RIOT gear: your online trail just got way more visible
By Tama Leaver, Curtin University
The recent publication of a leaked video demonstrating American security firm Raytheon’s social media mining tool RIOT (Rapid Information Overlay Technology) has rightly incensed individuals and online privacy groups.
In a nutshell, RIOT – already shared with US government and industry as part of a joint research and development effort in 2010 – uses social media traces to profile people’s activities, map their contacts, and predict their future activities.
Yet the most surprising thing isn’t how RIOT works, but that the information it mines is what we’ve each already shared publicly.
Getting to know you
In the above video, RIOT analyses social media accounts – specifically Facebook, Twitter, Gowalla and Foursquare – and profiles an individual.
In just a few seconds, RIOT manages to extract photographs as well are the times and exact location of frequently visited places. This information is then sorted and graphed, making it relatively easy to predict likely times and locations of future activity.
RIOT can also map an individual’s network of personal and professional connections. In the demonstration video, a Raytheon employee is surveyed, and the software shows who his friends are, where he’s been and, most ominously, predicts that the most likely time and place to find him is at a specific gym at 6am on a Monday morning.
Privacy concerns
The RIOT software quite rightly raises concerns about the way online information is being treated.
Since privacy rules and regulations around social media are still in their infancy, it’s hard to tell if any legal boundaries have been crossed. This is especially unclear since it appears, from the video at least, that RIOT only scrutinises information already publicly visible on the web.

The usefulness of some social media tools for mapping a person’s activity are abundantly clear. Foursquare, for example, basically produces a database of the times and places someone elects to “check-in” to specific locations.
Checking-in allows other Foursquare users to interact with that individual, but the record is basically a map of someone’s activities. Foursquare can be a great service, allowing social networking, discounts from businesses, and various location-based activities, but it also leaves a huge data trail.
Foursquare, though, has a (relatively) small user base (around 30 million) compared to Facebook (more than one billion) – although Facebook, as we know, also allows users to check-in by specifying a location in updates and posts. But the richest source of information we tend to share publicly, but not even think about, is our photographs.
Picture this
Every modern smartphone, whether an iPhone, Windows or Android device, by default saves certain information every time you take a photograph. This information about the photograph is saved using something called the Exchangeable image file format, or “exif” data.
Exif data typically includes camera settings, such as how long the camera lens was open and whether the flash fired, but on smartphones also includes the exact geographic location (latitude and longitude) and time that each photograph is taken.
Thus, all of those photographs of celebrations, birthdays, and our kids at the beach all include a digital record of where and when each and every event occurred.

Given that so many of us share photographs online using Facebook or Twitter or Instagram or Flickr, it’s not surprising that RIOT might be able to build a picture of where we’ve been and use that to guess where we might be in the future.
Yet we don’t have to leave this trail. Most smartphones have the ability to turn geographic location information off so that it’s not recorded when we take photographs.
Most of us never think to turn these options off because we don’t think about our social media persisting, but it does. Our social media fragments – our photos and posts – have no expiry date so it’s worth taking a moment when we set up a new phone or account and tweak the settings to only share what you really want to share.
If RIOT demonstrates anything, it’s the fact that information shared publicly online will likely be read, shared, copied, stored and analysed in ways we didn’t immediately think about.
If we take the time to adjust our privacy settings and sharing options, we can exercise some control over the sort of profile RIOT, or any future tool, might build about us.
Tama Leaver receives funding from the Australian Research Council.
![]()
This article was originally published at The Conversation. Read the original article.
Digital Culture Links: January 30th
Links for January 25th through January 30th:
- Twitter Is a Critical Tool in Republican Campaigns [NYTimes.com] – “When Newt Gingrich said in a recent debate that he was a man of “grandiose” ideas, Mitt Romney’s campaign pounced. It sent mocking Twitter messages with a hashtag, “#grandiosenewt”, encouraging voters to add their own examples of occasions when they felt Mr. Gingrich had been “grandiose.” Within minutes, the hashtag was trending on Twitter. Reporters picked up on it, sending out their own Twitter posts and writing their own articles. The result: for at least one news cycle, the Romney campaign had stamped a virtual “grandiose” on Mr. Gingrich’s forehead. If the 2008 presidential race embraced a 24/7 news cycle, four years later politicos are finding themselves in the middle of an election most starkly defined by Twitter, complete with 24-second news cycles and pithy bursts. With 100 million active users, more than 10 times as many as in the 2008 election, Twitter has emerged as a critical tool for political campaigns, allowing them to reach voters, gather data and respond …”
- Google CEO Larry Page: Identity Is A ‘Deep, Deep Part Of What We’re Doing’ [Huffington Post] – “Watch out: Google is getting personal. CEO Larry Page emphasized that Google is determined to deliver online experiences tailored to each individual’s interests and social circles, an ambitious goal that requires the web giant to learn even more about its users’ preferences and personal information. “Engaging with users, really deeply understanding who they are, and delivering things that make sense for them is really, really important. We’re at the early stages of that and Google+ is a big effort,” said Page during an earnings call Thursday. “This notion of identity is a deep, deep part of what we’re doing and an example of how we can make all our products better by understanding people.” Though Google already knows a great deal about the people who use its services, from what YouTube videos they’ve watched to whom they email most on Gmail, the web giant still lusts after the treasure trove of personal data Facebook has accumulated over the past eight years …”
- Twitter uncloaks a year’s worth of DMCA takedown notices, 4,410 in all [Ars Technica] – “On almost any given day, Twitter receives a handful of requests to delete tweets that link to pirated versions of copyrighted content—and quickly complies by erasing the offending tweets from its site. That fact itself is probably unsurprising to people familiar with the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) takedown process, which gives sites like Twitter a “safe harbor” against lawsuits related to user behavior and uploads—so long as the sites don’t knowingly tolerate pirated material or links to such material. But Twitter has taken the unusual step of making DMCA takedown notices public, in partnership with Chilling Effects, a project of the Electronic Frontier Foundation and several universities. […] Scrolling through recent takedown notices, you’ll see names like Magnolia Pictures, Simon and Schuster, Warner Music Group, Universal Music Group, among those of many other media companies.”
- Apple’s iPad and the Human Costs for Workers in China [NYTimes.com] – Long and important piece which looks at the poor working conditions in some of the factories which assemble and supply the parts for Apple’s most popular products. It balances the enormous profits Apple makes with the human cost which have, in some cases, led to worker suicide.
- MPAA Wins the Oscar Screener Battle, but Loses the War [Epicenter | Wired.com] – “Every year, the MPAA tries desperately to stop Oscar screeners — the review copies sent to Academy voters — from leaking online. And every year, teenage boys battling for street cred always seem to defeat whatever obstacles Hollywood throws at them. For the last 10 years, I’ve tracked the online distribution of Oscar-nominated films, going back to 2003. Using a number of sources (see below for methodology), I’ve compiled a massive spreadsheet, now updated to include 310 films. This year, for the first time, I’m calling it: The MPAA is winning the battle to stop screener leaks. A record 37 films were nominated this year, and the studios sent out screeners for all but four of them. But, so far, only eight of those 33 screeners have leaked online, a record low that continues the downward trend from last year. They may be winning the battle, but they’ve lost the war. While screeners declined in popularity, 34 of the nominated films (92 percent) were leaked online by nomination day …”
- Tweets still must flow [Twitter Blog] – Twitter starts blocking tweets nationally: “As we continue to grow internationally, we will enter countries that have different ideas about the contours of freedom of expression. Some differ so much from our ideas that we will not be able to exist there. Others are similar but, for historical or cultural reasons, restrict certain types of content, such as France or Germany, which ban pro-Nazi content. Until now, the only way we could take account of those countries’ limits was to remove content globally. Starting today, we give ourselves the ability to reactively withhold content from users in a specific country — while keeping it available in the rest of the world. We have also built in a way to communicate transparently to users when content is withheld, and why. We haven’t yet used this ability, but if and when we are required to withhold a Tweet in a specific country, we will attempt to let the user know, and we will clearly mark when the content has been withheld.”
- No More Résumés, Say Some Firms [WSJ.com] – “Union Square Ventures recently posted an opening for an investment analyst. Instead of asking for résumés, the New York venture-capital firm—which has invested in Twitter, Foursquare, Zynga and other technology companies—asked applicants to send links representing their “Web presence,” such as a Twitter account or Tumblr blog. Applicants also had to submit short videos demonstrating their interest in the position. Union Square says its process nets better-quality candidates —especially for a venture-capital operation that invests heavily in the Internet and social-media—and the firm plans to use it going forward to fill analyst positions and other jobs. Companies are increasingly relying on social networks such as LinkedIn, video profiles and online quizzes to gauge candidates’ suitability for a job. While most still request a résumé as part of the application package, some are bypassing the staid requirement altogether.”
- Online echo chambers: A study of 250 million Facebook users reveals the Web isn’t as polarized as we thought. – Slate Magazine – A large-scale controlled study of Facebook users and their sharing habits suggests that far from an echo chamber (our social networks reinforcing the views and interests of our strong ties), Facebook users appear to get as much information from their weak ties (ie not as good friends/acquaintances) and thus suggesting social networks introduce diversity of information and perspectives. [Read Eytan Bakshy’s Rethinking Information Diversity in Networks]
Digital Culture Links: January 25th
Links for January 25th:
- MEGAUPLOAD (by Dan Bull) – Independent artist Dan Bull raps about the harm shutting down MegaUpload has done to smaller artists. In the name of protecting the intellectual property of Hollywood and the MPAA, it seems that smaller artists who rely on cyberlockers like MegaUpload have found their means of distribution erased without noticed or recourse to protest.
- Star Wars crowdsourced film reaches million YouTube views [BBC News] – “A “directors cut” of a fan-made version of Star Wars has passed one million views on YouTube. The film, uploaded on 18 January, is made up of hundreds of 15-second scenes created by internet users. The Star Wars Uncut project is widely regarded as an example of the power of crowdsourcing. Ramon Youseph, of the Crowdsourcing Gazette blog, told the BBC it showed “the power of the web to engage people in a global collaborative effort”. The website starwarsuncut.com began asking for fan-made scenes in 2009. It went on to win an interactive media Emmy in 2010.”
- EU proposes ‘right to be forgotten’ by internet firms [BBC News] – A new law promising internet users the “right to be forgotten” will be proposed by the European Commission on Wednesday. It says people will be able to ask for data about them to be deleted and firms will have to comply unless there are “legitimate” grounds to retain it. […] A spokesman for the commissioner clarified that the action was designed to help teenagers and young adults manage their online reputations. “These rules are particularly aimed at young people as they are not always as aware as they could be about the consequence of putting photos and other information on social network websites, or about the various privacy settings available,” said Matthew Newman. He noted that this could cause problems later if the users had no way of deleting embarrassing material when applying for jobs. However, he stressed that it would not give them the right to ask for material such as their police or medical records to be deleted.”
- 60 hours per minute and 4 billion views a day on YouTube [YouTube Blog] – “Since the dawn of YouTube, we’ve been sharing the hours of video you upload every minute. In 2007 we started at six hours, then in 2010 we were at 24 hours, then 35, then 48, and now…60 hours of video every minute, an increase of more than 30 percent in the last eight months. In other words, you’re uploading one hour of video to YouTube every second.”
- How Parents Normalized Teen Password Sharing [danah boyd | apophenia] – Interesting insights from danah boyd regarding teens sharing passwords to social media services with each other. It’s all about trust, and that’s something learnt at home since parents ask kids to trust them and let parents look after (or at least know) their passwords in the early years (normally): “When teens share their passwords with friends or significant others, they regularly employ the language of trust, as Richtel noted in his story. Teens are drawing on experiences they’ve had in the home and shifting them into their peer groups in order to understand how their relationships make sense in a broader context. This shouldn’t be surprising to anyone because this is all-too-common for teen practices. Household norms shape peer norms.”
- Defend our freedom to share (or why SOPA is a bad idea) [YouTube] – A great talk from Clay Shirky explaining the history, context and potential impact of the US SOPA and PIPA bills which seek to radically censor the internet in the name of stopping “piracy”. Important to listen to since, as Shirky argues, there’s no doubt more of the same just around the corner.
Digital Culture Links: January 21st
Links for January 21st:
- iBooks Textbooks for iPad [Apple – Education] – Apple jumps into the textbook market, with impressive pricing and engaging looking media-rich books which, of course, rely on students already owning an iPad. However, with a proprietary book creation tool, iBooks and a supposedly course-encompassing tool iTunes U which reduces education to content provision, at the very least Apple’s latest entry into education will need to be carefully contextualised and managed by educators. Kathleen Fitzpatrick highlights some other important concerns, too.
- US prosecutors shut down one of world’s largest file-sharing sites, Megaupload [The Washington Post] – “One of the world’s largest file-sharing sites was shut down Thursday, and its founder and several company executives were charged with violating piracy laws, federal prosecutors said. An indictment accuses Megaupload.com of costing copyright holders more than $500 million in lost revenue from pirated films and other content. The indictment was unsealed one day after websites including Wikipedia and Craigslist shut down in protest of two congressional proposals intended to thwart online piracy. The Justice Department said in a statement said that Kim Dotcom, formerly known as Kim Schmitz, and three others were arrested Thursday in New Zealand at the request of U.S. officials. Two other defendants are at large. Megaupload was unique not only because of its massive size and the volume of downloaded content, but also because it had high-profile support from celebrities, musicians and other content producers who are most often the victims of copyright infringement and piracy.”
- Eastman Kodak files for bankruptcy protection [BBC News] – “Eastman Kodak, the company that invented the hand-held camera, has filed for bankruptcy protection. The move gives the company time to reorganise itself without facing its creditors, and Kodak said that it would mean business as normal for customers. The company has recently moved away from cameras to refocus on making printers, to stem falling profits. The 133-year-old firm has struggled to keep up with competitors who were quicker to adapt to the digital era. “Kodak made all its money from selling film, then the digital camera came along and now no-ones buying film. It’s not like they didn’t see it coming. Kodak hesitated because they didn’t want to eviscerate their business,” said Rupert Goodwins, editor of technology website ZDNet.” For visuals, see [The Guardian’s Kodachrome Photo Retrospective]
- Teenagers Sharing Passwords as Show of Affection [NYTimes.com] – “Young couples have long signaled their devotion to each other by various means — the gift of a letterman jacket, or an exchange of class rings or ID bracelets. Best friends share locker combinations. The digital era has given rise to a more intimate custom. It has become fashionable for young people to express their affection for each other by sharing their passwords to e-mail, Facebook and other accounts. Boyfriends and girlfriends sometimes even create identical passwords, and let each other read their private e-mails and texts. They say they know such digital entanglements are risky, because a souring relationship can lead to people using online secrets against each other. But that, they say, is part of what makes the symbolism of the shared password so powerful.”
- Facebook: Making Your Political Opinions Less Private Since 2012 [Blog of Rights: Official Blog of the American Civil Liberties Union] – “Facebook announced yesterday that “every post and comment — both public and private — by a U.S. user that mentions a presidential candidate’s name will be fed through a sentiment analysis tool that spits out anonymized measures of the general U.S. Facebook population.” This analysis, along with reader polls and other information, will in turn be shared with politico.com. The brief announcement of this new feature raises serious questions and offers few answers. Most troubling is Facebook’s willingness to search and collect users’ private political preferences and thoughts, preferences they may have shared only with their closest friend in a private email. This raises at least three concerns. The first is that many users may not want to be part of any “sentiment analysis” or poll …”
Digital Culture Links: January 12th
Links for January 1st through January 12th:
- Amazon Launches iPad Kindle Store to Dodge Apple’s Restrictions [RWW] – Amazon launches even further into Apple’s regulated home turf: “Amazon has launched a more touch-friendly, Web-based iPad Kindle Store. A tablet-optimized Kindle store was available through the HTML5 Kindle Cloud Reader Amazon launched last August, but the new iPad Kindle Store is a standalone Web app. Upon visiting amazon.com/iPadKindleStore from Safari, a pop-up prompts the user to add it to the home screen. This is the most seamless way for Kindle users to buy books on the iPad. Apple’s in-app purchasing rules prevent e-book sellers from offering stores in their native apps (without giving Apple a 30% cut). The route around that was to include a link to the Web store inside the native reader app. Last July, Apple forced Amazon and other e-reader apps to remove this link, so users of e-book platforms other than Apple’s iBooks must buy their books in the browser, in a separate place from where they read.”
- Search, plus Your World [Inside Google Search]– Google adds more personalisation with “Search, plus Your World” which heavily (but OPTIONALLY) integrates Google+ and other social search results into the first page results when searching Google (if signed in to Google+).Twitter (and presumably Facebook) are unhappy since this competes with their social search roles, but Google have responded that this seems a bit rich since Twitter refused to let Google pay to index Twitter in realtime.
- Angry Birds named most downloaded paid app [Think Digit] – “Rovio’s Angry Birds has been named the most downloaded paid app for the smartphones and tablets in 2011. According to research firm Distimo, Angry Birds was downloaded more than any other application across all major operating systems including Android, iOS, Windows Phone and others. The only platform missing out on the list is BlackBerry. However, the game was recently made available on the BlackBerry’s App World. Angry Birds was followed by Fruit Ninja, while another variant of Angry Birds, Angry Birds Season grabbed the third spot on the list of the paid apps for the year 2011. Among the free apps, Facebook grabbed the top spot, while Pandora Radio followed at the second spot. The free versions of Word with Friends and Angry Birds remained on third and fourth position respectively. The Distimo report covers data collected from January to November 2011. The report has various notable findings such as Apple App Store has four times more revenue than Google’s Android Market.”
- Digital Music Sales Surpass Physical Music Sales For the First Time Ever [Moneyland | TIME.com] – “Last year, for the first time in history, digital music sales exceeded physical sales, according to a newly released Nielsen/Billboard report cited by CNNMoney. In 2011, digital music sales climbed past physical sales to take a 50.3% market share of all music purchases. In a continuation of a multi-year trend, digital sales increased by 8.4% from 2010, while physical sales declined 5%.
In the decade since Apple launched its iTunes music store, a host of digital music ventures have appeared, with varying degrees of success. iTunes remains the market leader but faces increasing competition from upstarts like Rdio, Spotify and Pandora, which went public earlier this year.” - Angry Birds bags 6.5m Christmas Day downloads [guardian.co.uk] – Rovio Mobile says its three Angry Birds games generated 6.5m downloads on Christmas Day alone. The company’s vice president of franchise development Ville Heijari revealed the milestone to All Things Digital, while promising new games in the year ahead. “We’re really excited to have such a massive number of new people get acquainted with Angry Birds over the holidays – we have exciting new releases lined up for 2012, and can’t wait to introduce them to the public,” said Heijari. He did not break down the 6.5m figure by game – Angry Birds, Angry Birds Seasons and Angry Birds Rio are the three available titles – nor did he split them out by platform. While the lion’s share are likely to have come from iOS and Android, Angry Birds is also available on Windows Phone, while all three games are available for Nokia handsets and RIM’s BlackBerry PlayBook tablet.” Angry Birds was downloaded more than 600 million times in 2011, with over a million branded toy and shirt sales each month.
- Facebook Blamed For a Third of British Divorces [MediaCity] – “So Facebook is again at the other end of the blame-hammer, this time for precipitating about a third of divorces in Britain. The stats come from a website- the UK’s Divorce-Online, and cull stats from 5,000 divorce petitions. The same stats were pulled in 2009, and at that time, Facebook made an appearance in 20% of the petitions. Infidelity-related complaints were a forerunner, along with using Facebook walls to make nasty comments about soon to be exes.”
- The PostSecret App is Now Closed [PostSecret] – The PostSecret App (iPhone/iPad) closes after anonymous posts and comments prove unmanageable as part of a confessional community. (The closed app is now dubbed an “experimental community” that failed. Despite being a paid app, there is no mention, or apology, to those who paid for it in good faith.) From the PostSecret blog: “Like the PostSecret Blog, the App was designed so each secret was absolutely anonymous. Unfortunately, that absolute anonymity made it very challenging to permanently remove determined users with malicious intent. 99% of the secrets created were in the spirit of PostSecret. Unfortunately, the scale of secrets was so large that even 1% of bad content was overwhelming for our dedicated team of volunteer moderators who worked 24 hours a day 7 days a week removing content that was not just pornographic but also gruesome and at times threatening.”
- Year in Review: 2011 in Numbers [Instagram] – “We’ve seen the Instagram community grow from 1 million to over 15 million users in 2011. To celebrate, we’re recapping the year’s activity in our Year in Review series.
Accounts
1 million: The number of accounts on Jan 1, 2011.
15 million (and counting): The number of accounts on Jan 1, 2012.
Photos
3: The average number of photos uploaded per second, one year ago.
60: The average number of photos uploaded per second, today.
400 million: The total number of photos shared on Instagram so far.”
Digital Culture Links: November 17th
Links for November 12th through November 17th:
- An Oscar for Andy? by Tama Leaver [Antenna] – My first Antenna post looks at the possibility of a synthespian in the running for an acting Oscar: “On the back of the unexpected success of Rise of the Planet of the Apes, the big news isn’t a planned sequel but rather a “a healthy seven-figure deal for Andy Serkis to reprise his role as lead ape Caesar” along with the announcement that 20th Century Fox will be mounting an Oscar campaign aimed at getting Serkis a long overdue nod for Best Supporting Actor. It’s significant, too, because we never see Andy Serkis directly in Rise; rather, Caesar was created by the meshing of Serkis’s visceral, physical acting and the state-of-the-art computer wizardry from Weta Digital. Whether you prefer the term virtual actor, synthespian (‘synthetic thespian’) or just performance capture, an Academy Award for Serkis would demonstrate a widening understanding of what ‘acting’ actually means.”
- Google Music is open for business [Official Google Blog] – Google’s competitor to Apple’s iTunes has gone live, cleverly basing itself in the Android store. Of course, it’s not yet available in Australia.
- Salman Rushdie claims victory in Facebook name battle [BBC News ] – “Author Salman Rushdie says he has won a battle with Facebook over what to call himself on his profile page on the social network. Rushdie’s dispute with Facebook began after he asked to be allowed to use his middle name Salman – the one he is known by across the world. But Facebook, which has strict real name policies, had insisted on Ahmed – the novelist’s first name. Rushdie says Facebook has “buckled” after he began tweeting about the row. “Victory! #Facebook has buckled! I’m Salman Rushdie again. I feel SO much better. An identity crisis at my age is no fun. Thank you Twitter!” wrote the British Indian author, who is known as SalmanRushdie on Twitter. “Just received an apology from The #Facebook Team. All is sweetness and light.””
- Aussie expat’s TV torrent site shut down as The Slap producers intervene [SMH] – “The producers of ABC1 drama The Slap have succeeded in shutting down a Netherlands-based piracy website that over 40,000 Australian and New Zealand expats use to illegally watch local shows. The site, diwana.org, is run by an Australian expat who started the site over five years ago and is popular with expats and others based overseas who are looking to access Australia and New Zealand TV content, which is often difficult to access internationally.[…] Despite the shutdown of Diwana.org, The Slap is still widely available on other pirate websites.”
- Exfoliate for Facebook [Android Market] – Android app to delete unwanted Facebook history: “Exfoliate automates the removal of old, forgotten, content from Facebook(tm). Old content on social networking sites is a threat to your privacy. Removing this old content by hand is tedious, and practically impossible. On your wall, Exfoliate can remove any post, comment, or like, whether made by you or by others, older than a time you specify. Exfoliate can remove your own posts, comments, and likes, from your friends’ walls too. You can choose the age of items you wish removed, and Exfoliate will remove any items that are at least as old as your selection from any of your selected content areas. It is important, though, to understand that Exfoliate truly deletes the content. It is not backed up and it is not recoverable – well, that’s kinda the point. […] Exfoliate is a network and battery hog, and there’s simply no way around this. To manage the impact, you can stop Exfoliate at any time, and restart Exfoliate later.”
- Jailbreak the Patriarchy: my first Chrome extension [Danielle Sucher] – Clever: “I just released my first Chrome extension! It’s called Jailbreak the Patriarchy, and if you’re running Chrome, you can head over here to install it. What does it do? Jailbreak the Patriarchy genderswaps the world for you. When it’s installed, everything you read in Chrome (except for gmail, so far) loads with pronouns and a reasonably thorough set of other gendered words swapped. For example: “he loved his mother very much” would read as “she loved her father very much”, “the patriarchy also hurts men” would read as “the matriarchy also hurts women”, that sort of thing. This makes reading stuff on the internet a pretty fascinating and eye-opening experience, I must say. What would the world be like if we reversed the way we speak about women and men? Well, now you can find out!”
Digital Culture Links: October 31st through November 4th
Links for October 31st through November 4th:
- Anonymous online comments [The Age] – “Online news readers should be forced to reveal their identity when commenting on a story, a parliamentarian has argued while complaining about West Australian’s poor online behaviour. WA Labor MP Andrew Waddell called on news websites, including this one, to publish readers’ names with their post. “It has become an unfortunate fact that there is a group of cowards who, hiding behind the veil of anonymity, abuse their right to free speech to perpetuate lies, abuse others, commit hate crimes, libel others and behave in an unacceptable manner,” Mr Waddell told parliament yesterday. “It is often possible to post a comment on a very public site without there being any need to provide real validated identification. This gives … courage to those who may not otherwise be willing to stand behind their comments and face the consequences of their opinions. “A vibrant society has a healthy ongoing political debate … [but] vicious, nasty, anonymous trolls have no place in that debate.”
- Man jailed for posting sex images of ex-partner online [BBC News] – “”A Nottingham man who posted sexual images of his former girlfriend online as he stalked her via social networking sites has been jailed for four months. Shane Webber, 23, of Hodgkin Close in Clifton, sent photographs and personal details about Ruth Jeffery, 22, to her family and strangers. Webber admitted one count of harassment at an earlier hearing at Southampton Magistrates’ Court. Miss Jeffery said she was devastated by Webber’s actions. Outside court she said even if Webber had received the maximum jail sentence magistrates could impose – six months – it would not have made up for the hurt she had been caused. She said: “I am extremely pleased with the outcome. The maximum sentence in a magistrates’ court will never make up for the hurt he had put me through but I am pleased I can now put it behind me.”
- Q&A: Felicia Day, from ‘The Guild’ to ‘Dragon Age’ [latimes.com] – “Playing” Felicia Day: “And when Electric Arts [makers of Dragon Age] called, that was the first call in years that was really like, “Oh!” They asked, “What would you like to do?” and I said, “What properties do you have?” And when Dragon Age came up I was, like, “Yes!” Because when am I ever going to be able to be in a medieval world as an actor? Probably never. So I’ll help create it myself. This will be the first time that a video game property is a Web series; and the elf is an actual playable character. So my character will be a DLC [downloadable content] piece; if people own Dragon Age II, they’ll be able to purchase an extension pack and play with my character. It’s full motion capture with me, full facial capture, full vocal acting. It’s pretty much the coolest thing I could ever imagine: Not only am I in a game, but it’s as a character I created.”
- Angry Birds smashes half a billion downloads! [YouTube] – Cute little video with statistics about Angry Birds including the big one: half a billion downloads so far. That’s an awful lot! (Personally, I can account for 5 of those – 3 on Android, 2 on the iPad!)
- Plagiarism [Common Craft] – Basic but very accessible and useful video explaining plagiarism: “While Plagiarism can be intentional, it is more often caused by misunderstanding. Avoiding it means understanding the role of intellectual property and what makes plagiarism wrong. This video teaches: Why giving credit to others is necessary; A definition of plagiarism; Steps to avoiding plagiarism; Types of ideas and media that can be plagiarized”
- BBC News – Man jailed for posting sex images of ex-partner online – “A Nottingham man who posted sexual images of his former girlfriend online as he stalked her via social networking sites has been jailed for four months. Shane Webber, 23, of Hodgkin Close in Clifton, sent photographs and personal details about Ruth Jeffery, 22, to her family and strangers. Webber admitted one count of harassment at an earlier hearing at Southampton Magistrates’ Court. Miss Jeffery said she was devastated by Webber’s actions. Outside court she said even if Webber had received the maximum jail sentence magistrates could impose – six months – it would not have made up for the hurt she had been caused. She said: “I am extremely pleased with the outcome. The maximum sentence in a magistrates’ court will never make up for the hurt he had put me through but I am pleased I can now put it behind me.”
- Angry Birds developer Rovio to open stores in China [BBC News] – Angry Birds maker Rovio has announced plans to open stores in China within 12 months. Unofficial merchandise connected to the videogame has already proved popular in the country. The company’s chief marketing officer, Peter Vesterbacka, made the announcement at the Techcrunch conference in Beijing. He said he was targeting $100m (£62m) in sales from the shops in their first year of operation. “On the physical side, we don’t have a lot of our officially licensed products out here, so we have ourselves to blame,” he told the conference. Mr Vesterbacka said he had been to China many times “checking out the Angry Birds’ presence”. He told delegates he was unhappy with the quality of the unofficial products, but had also gained “a lot of inspiration from the copyists”. The comment drew laughter from the audience.”
- Qantas’ Social Media Response Rapped For Bad Service [The Age] – “Qantas has been criticised for its mechanical, impersonal social media response to the grounding of its fleet and the ensuing customer chaos. The announcement sparked a torrent of posts on Twitter, with independent social media analyst Thomas Tudehope noting that, at its peak, “Alan Joyce”, “Qantas” and “Anthony Albanese” were all trending worldwide – indicating in excess of a thousand tweets per minute. “This is particularly remarkable given that Australia only has an estimated 2 million Twitter accounts compared to a global audience pushing towards 250 million accounts,” Tudehope said. […] Several Twitter accounts have sprung up lampooning Qantas and its CEO, Alan Joyce, including @AlanJoyceCEO and @Qantas_VH_OQA.”
Digital Culture Links: October 30th 2011
Links for October 30th 2011:
- Cashing In on Your Hit YouTube Video [NYTimes.com] – In the unlikely but not impossible event of a YouTube video going unexpectedly viral, here’s a quick guide from the New York Times on how to act quickly and make the most of your possible revenue and exposure.
- When I died on Wikipedia | David McKie [The Guardian] – Amusing and insightful column from David McKie who Wikipedia incorrectly claimed, was dead. McKie points out that the Wikipedia is far from the first media service to prematurely announce people’s demise: “It was disconcerting to learn recently from a much used reference source that I had died on Friday August the 26th. True, one’s memory gets more fitful as one grows older, but I didn’t remember this happening. When I looked that day up in my diary, I found that I had noted it down as “a very empty day” when it rained and nothing much happened. Empty, perhaps, but not as empty as that. Still, there it was, in all its bleak finality, in a summary on Wikipedia: “David McKie (1935 – 26 August 2011) was a British journalist and historian.” […] Wikipedia, I see, welcomes corrections. Indeed, its section on premature obituaries accepts it is incomplete and appeals for more, well-sourced, entries. So now I shall write to correct their error …”
- Untangling the web: how the internet has changed the way we treat death [Technology | The Observer] – Good overview by Aleks Krotoski looking at death in a networked, digital world: “Death in the age of the web reminds us how much the technology has become part of the fabric of our personal and social identities. Once we’re gone, what we leave behind is a rich resource of who we are. We may not survive beyond the release of the next social network, but our inevitable ends are being extended by our digital lives.”
- @AlanJoyce abused on Twitter, but he’s not the Qantas boss [Perth Now] – “An American science student who shares his name with the CEO of Qantas has found himself the target of a deluge of abuse on Twitter. The unfortunate American, whose name is Alan Joyce and who holds the name @alanjoyce on Twitter, is currently studying computer science at Stanford University, as well as having written two guidebooks to the Disneyland Resort in California. To clarify his identity the American replied to one accusation: “I’m glad to see someone appreciating my impeccable American accent, but I’m guessing you’re looking for a different Alan Joyce.” […] The American Alan Joyce first responded to the attacks after @DognutsTom tweeted, “Well I’m stuck at home with broken wheelchair thanks to QANTAS! You think @alanjoyce CEO of QANTAS could work it out right?” Alan replied, “Sorry about your wheelchair, but I’m no more CEO of Qantas than @willsmith is a famous movie actor.””
- Q&A;: Felicia Day, from ‘The Guild’ to ‘Dragon Age’ [latimes.com] – “Playing” Felicia Day: “And when Electric Arts [makers of Dragon Age] called, that was the first call in years that was really like, “Oh!” They asked, “What would you like to do?” and I said, “What properties do you have?” And when Dragon Age came up I was, like, “Yes!” Because when am I ever going to be able to be in a medieval world as an actor? Probably never. So I’ll help create it myself. This will be the first time that a video game property is a Web series; and the elf is an actual playable character. So my character will be a DLC [downloadable content] piece; if people own Dragon Age II, they’ll be able to purchase an extension pack and play with my character. It’s full motion capture with me, full facial capture, full vocal acting. It’s pretty much the coolest thing I could ever imagine: Not only am I in a game, but it’s as a character I created.”
Reputation Management and Social Media
Today the Pew Research Centre’s Internet and American Life Project released their report Reputation Management and Social Media (2010) which is based on research undertaken late 2009. There is a great deal of important and topical information in the survey, with the US results likely to be slightly higher but certainly comparable to trends in Australia. I want to really draw attention to the way that younger adults are using social media according to this report, using three of Pew’s graphs to talk about their findings.
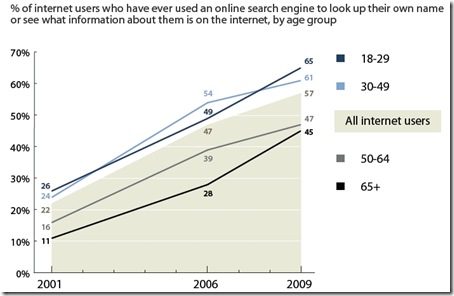
The first graph indicates how many internet users search for their own name online:
This result is particularly interesting for two reasons: firstly, it shows that across the board, interest in our own web presences has increased dramatically across the last decade; and secondly, it highlights that younger adults (those 18-29) appear to be the most concerned with their online reputation. As danah boyd celebrated earlier today, this result really undermines the cultural myth that younger people are the least interested with online privacy. Obviously this survey excludes people under-18, but it’s fair to assume that part of the process of growing up these days includes becoming sensitised to the importance of being aware of our web presence.
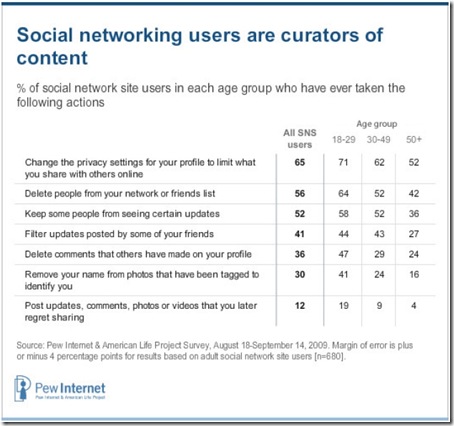
Similarly, the Pew report also highlights the face that younger people are the most active in controlling their presence online, insomuch as they are most likely to have changed their privacy settings on social networks, they are the most likely to untag a photo of themselves, and so forth:
Here we see that younger people are also the most conscious of shaping their web presence, by editing who can see what they share online, and which elements of the digital artefacts linked to them remain visible, and remain linked to their names.
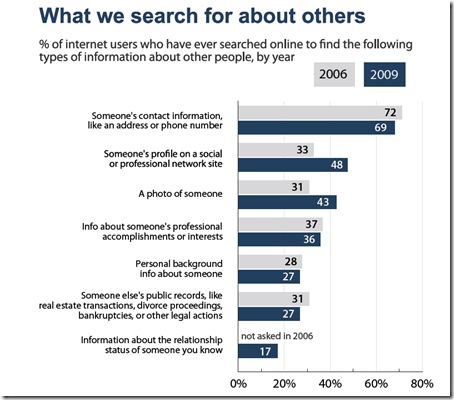
The last Pew graph shows how much information people are seeking about others online:
Everything from contact details to photos are being sought online, which similarly highlights how important it is that everyone be aware of what their web presence really ‘says’ about them.
Since I teach in the Internet Studies department here at Curtin, it’s hardly a surprise that all of this information is vital to consider when we design the learning experiences our students encounter. In the first-year unit Web Communications 101, the notion of web presence is our central organising theme. However, one of the distinctions we make, which Pew does not, is the difference between digital traces we leave purposefully, and maintain control over, versus those we don’t. In Web Comms 101, as Pew does, we talk about footprints, but we also talk about digital shadows, those bits of digital media that are somehow attached to our names, or chosen identities, which we have minimal, if any, control over. Given how much people search for each other, and how much thought is going into how we appear online for the average internet user, it’s probably how we address and deal with those shadows which will be one of the most important topics to seriously consider in the coming years.