takethislollipop.com: Creepy Personalised Facebook Stalker Short Film!
Just in time for All Hallow’s Eve comes takethislollipop.com an extremely clever and deeply unsettling personalised short film experience. The short asks you to share your Facebook data, then imports images, personal details and geographic information to customize a stalking experience just for you! The resulting short (which takes just a few seconds to generate) uses very clever graphics and a recognisable but well-shot set-up that would be right at home in one of the endless torture porn movies gracing cinemas in the last few years. It’s all about you, and a very creepy guy who has decided to come and find you …

I can’t imagine Take This Lollipop will do much to ease fears about cyberstalking, nor will it win fans who hold privacy concerns (the film DOES access all of your Facebook data – they promise not to keep it, but I revoked the app’s access as soon as I’d seen the short). It is, however, VERY effective. It’s also fun to imagine this stalker is an advertising executive who works closely with Facebook … ![]()
Digital Culture Links: October 17th 2011
Links for October 5th 2011 through October 17th 2011 (catching up on a backlog of good links!):
- New YouTube features for music artists [YouTube Blog] – YouTube gets even further on the disintermediation bandwagon (ie cutting out the middle people), letting bands and music partners offer merchandising, concert tickets and link to digital sales (including iTunes) from their music videos. It’s all about the integration!
- Amazon Rewrites the Rules of Book Publishing [NYTimes.com] – “Amazon.com has taught readers that they do not need bookstores. Now it is encouraging writers to cast aside their publishers. Amazon will publish 122 books this fall in an array of genres, in both physical and e-book form. It is a striking acceleration of the retailer’s fledging publishing program that will place Amazon squarely in competition with the New York houses that are also its most prominent suppliers. It has set up a flagship line run by a publishing veteran, Laurence Kirshbaum, to bring out brand-name fiction and nonfiction. It signed its first deal with the self-help author Tim Ferriss. Last week it announced a memoir by the actress and director Penny Marshall, for which it paid $800,000, a person with direct knowledge of the deal said. Publishers say Amazon is aggressively wooing some of their top authors. And the company is gnawing away at the services that publishers, critics and agents used to provide.”
- Buyers dodge court’s Samsung tablet ban [The Age] – Surprising no one: “Australians are making a mockery of a Federal Court injunction banning the sale of Samsung Galaxy Tab 10.1 tablets in Australia by ordering them from online stores. Meanwhile, in the US, Samsung’s own lawyers were left red-faced after being unable to differentiate between Samsung’s and Apple’s tablets in court. Samsung has been forbidden by Federal Court Justice Annabelle Bennett from selling or marketing the device in Australia until a full hearing in its patent infringement case with Apple, which isn’t expected to take place until next year. Justice Bennett said Apple had a prima facie case that Samsung infringed two of its patents. But online sellers on eBay, and web stores such as MobiCity.com.au, Expansys, Techrific and dMavo, are bypassing Samsung Australia and obtaining stock from other countries, such as Hong Kong.”
- Google Announces Third Quarter 2011 Financial Results (GooglePlus = 40 million+) [Google Investor Relations] – In their third quarter financial resuts, Larry Page announces that Goole+ has passed 40 million users.
- Lady Gaga bans Lady Goo Goo song [BBC News] – Given Lady Gaga’s rhetoric about respecting her fans ignoring (her) copyright and that this effort seems like parody to me, I’ll be interested to see how this is justified: “Lady Gaga has won an injunction at London’s High Court to stop animated character Lady Goo Goo from releasing a single, its makers have said. Lady Goo Goo, a baby with a long blonde fringe from the Moshi Monsters online game – owned by UK firm Mind Candy – released The Moshi Dance on YouTube. But Lady Gaga’s injunction has stopped its full release, Mind Candy said. Law firm Mishcon de Reya confirmed it had represented Lady Gaga but said it could not comment further.”
- A fall sweep [Official Google Blog] – Google is killing off a number of poorly performing products. Google Buzz is the most notable closure. Hopefully Google learnt a lot from Buzz, especially about privacy.
- Felicia Day turns to Hangouts to promote new show [NewTeeVee – Online Video News] – “Web series veteran Felicia Day will promote her new online show Dragon Age: Redemption with a unique twist on Google+ Hangouts: The actress will be experimenting with something she dubbed Hangout Housecalls this coming Tuesday. Day is promising to visit as many Hangouts of her fans within a three-hour window as possible. She announced the house calls on Google+, where she explained: I’ll answer questions about the show and we can even pose for a photo that you can screencap and post later! Cool? Cool. The Dragon Age: Redemption house calls will kick off with a post on Day’s Google+ profile on Tuesday at 10 a.m. PST that will ask viewers to post links to their Hangouts in the comments. Day will then click through those links, visiting one Hangout after another.”
- The Guild turns product placement into merchandising gold [NewTeeVee – Online Video News] – Good wrap-up of the many, many different types of merchandise now available surrounding Felicia Day’s web series The Guild. Also interesting are both the careful deals – finding merchandise options which don’t threaten existing sponsorship from Microsoft and Sprint – but also how a lot of merchandise was strategically linked to Comic Conventions so that, eventually, they could be integrated into Season Five of The Guild which is largely set at a con. Day really is a canny business person and shows how far a recognisable web series can the deployed to make money across a wide range of products and tie-ins.
- 200 million Creative Commons photos and counting! [Flickr Blog] – Flickr users have now explicitly licensed and shared over 200 million photos using Creative Commons licenses. This is a fantastic and valuable resource. However, given there are more than 5 billion photos on Flickr, surely there could be more under CC licenses if the world was really spread? After all, being able to specify your license is one of the key things that Facebook really can’t do right now/
- Barcode Scanner for Zotero [Android App] – Android barcode scanning app for Zotero. If the barcode links to a book metadata, you can automatically add it to your Zotero library. “Scanner For Zotero brings Zotero’s magic wand tool out into the physical world. Scan the ISBN barcode on any book, and Scanner For Zotero will fetch that item’s bibliographic info from the web and allow you to add it to your Zotero library.That’s pretty cool.”
- Facebook’s privacy lie: Aussie exposes ‘tracking’ as new patent uncovered [The Age] – “Facebook has been caught telling porkies by an Australian technologist whose revelations that the site tracks its 800 million users even when they are logged out have embroiled Facebook in a global public policy – and legal – nightmare. Facebook’s assurances that “we have no interest in tracking people” have been laid bare by a new Facebook patent, dated this month, that describes a method “for tracking information about the activities of users of a social networking system while on another domain”.”
The Ends of Online Identity – Presentation
Here are the slides and audio for my ‘The Ends of Online Identity’ paper (abstract) I’m presenting in a couple of hours here at Internet Research 12 in Seattle:
I’ll try and record the talk and if it’s decent quality, I’ll synchronise the audio and slides as soon as I get a chance. Update: the audio turned out okay, so it’s now synchronised with the slides. If you’re interested, have a listen. I’d love to hear your thoughts and responses!
Digital Culture Links: October 3rd 2011
Links for September 27th 2011 through October 3rd 2011:
- How Social Networking Is Reviving Communal TV Viewing [The Next Web] – Real-time TV viewing is on the rise once more thanks to cleverly design related apps and strategic use of related #hashtags: “There are some signs that TV’s re-engaging its most coveted viewers. According to Nielsen, tech-savvy 12-24 year-olds are more connected and therefore more adept at using mobile devices to watch shows. This doesn’t bode well for the networks or for advertisers since, sometimes, the ads can be skipped. However, by turning TV programming into a true two-screen experience, it changes the equation. It makes the live experience more valuable, especially for the younger set. The data show that 18-34 year-olds are the most active demographic on social networks.”
- Facebook sued over claims it tracks users’ activity [The Age] – “Facebook is being sued by a group of users over claims it tracks their online activity after they log off. […] On Friday, 10 public interest groups asked the US Federal Trade Commission to investigate Facebook’s tracking of internet users after they log off. They urged the commission to examine whether Facebook’s new ticker and timeline features increased privacy risks for users by combining biographical information in an easily accessible format. The lawsuit – filed by Perrin Aikens Davis, of Illinois – seeks class status on behalf of other Facebook users in the US. Davis seeks unspecified damages and a court order blocking the tracking based on violations of federal laws, including restrictions on wiretapping, as well as computer fraud and abuse statutes.”
- Peers, review your actions [Times Higher Education ] – Interesting proposition: academics should boycott doing peer review (for free) for journals which aren’t open access (ie charge a lot to be viewed).
- Princeton goes open access to stop staff handing all copyright to journals – unless waiver granted [The Conversation] – Princeton University policy prevents their academics from publishing in journals which demand full copyright over their work (unless explicit permission is sought from the institution). A bold move to try and reign in the big copyright holders and publishers who currently have a strangle-hold over a great deal of academic work!
- BBC iPlayer launches on iPad in Australia [TV Tonight] – The BBC iPlayer comes to Australia, for a fee. For $10 a month you can access more than 1000 hours of BBC archives (at launch, growing regularly) but NOT current TV shows. In part this is probably due to existing contracts with local networks (why would the ABC bother to screen Doctor Who if it was available via iPlayer before broadcast), but this really doesn’t then address the problem of the tyranny of digital distance. This is a clever commercial move, but is unlikely to address the issue of unauthroised downloading of UK TV shows in Australia.
- A New Flavor…Still Delicious [AVOS] – AVOS launch the re-imagined Delicious. Being a long-term Delicious user, I’ve got to admit I find the new version a bit confronting, especially the changes to tag clouds and so forth. And I really don’t want “stacks” – that’s what something like Pinterest is for (and I don’t use that much, either). However, I’m delighted Delicious lives on, so I’ll give it a go!
Facebook’s New Timeline & Perceptions of Privacy
Everyone’s Facebook profile will disappear in 6 October 2011, December 2011 replaced with a Timeline. Here are my thoughts and concerns about that Timeline, and some suggestions about managing your Timeline when it arrives …
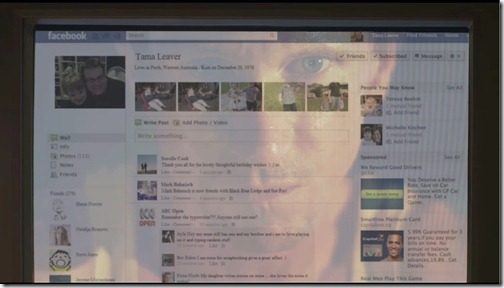
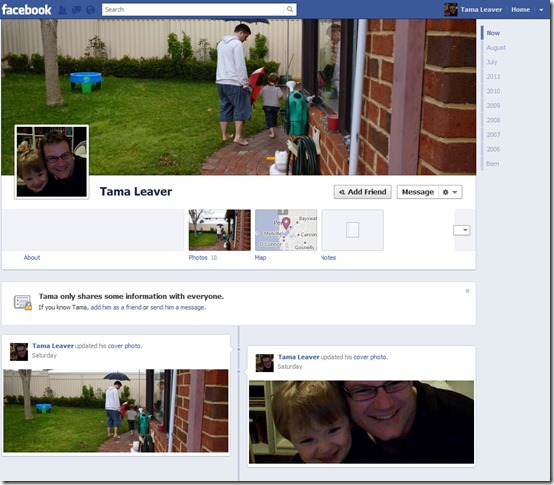
I’ve been testing out Facebook’s new Timeline which will shortly replace profiles for all 800 million Facebook users. I have some concerns which I’ll outline in a minute, but I have to give credit where credit is due: Timeline looks amazing. I think this is the first time Facebook has stopped looking like a direct descendant of the profiles found on online dating websites! The new cover image, which is separate from your avatar or profile picture, stretches across the entire screen and is much more richly visual experience, combined with far better navigation tools for exploring the entirety of someone’s Facebook history, not just their current statuses and photos. Here’s what the top of my Timeline looks like:
The tools which allow you to emphasise certain events on your timeline let individuals build an engaging and carefully curated story of themselves. And in a move which deliberately situates Facebook as telling the story of your life, Timeline actively encourages users to add in missing details. When I look at the notification of my 2000 university graduation, Timeline suggests I add to the story and post a picture, enriching the tale visually. If I add a picture, then the event ‘looks’ more interesting and is more engaging than a bit of text in an ‘Info’ box. However, in moving from being primarily about current communication to adding the archival/historical emphasis, a number of privacy-related issues arise.
My Timeline image above is missing a lot of detail since it’s the view that the public can see – ie someone who I’m not connecting to at all – and my privacy settings are high (almost everything is ‘Friends Only’; incidentally, once your Timeline is visible you can use the right-hand setting indicator – the one that looks like a wheel – and select ‘View as …’ to check how your Timeline will look to anyone else, including the public view). It’s notable, then, that the cover photo — the big one, at the top of your Timeline, which isn’t your profile photo — joins your profile photo as an image that you can’t make private; if you can be found on Facebook, it’s there. (I presume this might disappear if you prevented your profile being found in searches, but I can’t say that definitively.) Profile pictures have been unavoidably public for a while, so we just need to remember this about cover photos, too.
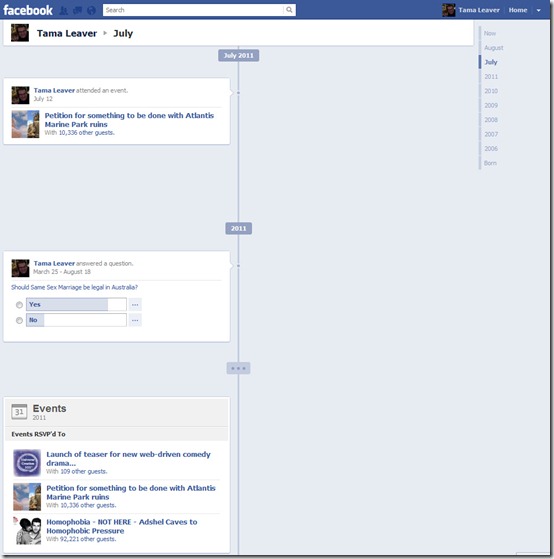
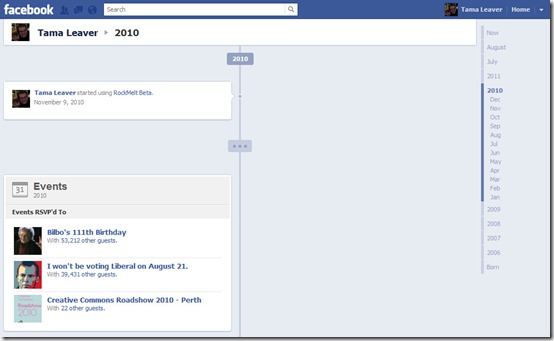
If you scroll down my Timeline (which, as I said, is now absurdly easy with the right hand date-based navigation tools) this is what you can see for 2011 and 2010 (there’s not much there, but take a look at what is visible):
On some abstract level, I was aware that when I ‘voted’ or clicked ‘Attending’ I was committing to something that was visible beyond my immediate ‘friend’ network (notable for me since, due to my privacy settings, not much else is). However, most of these actions or events had, from my perspective, long since ‘disappeared’ to the extent that, in order to find them, someone would have to click to ‘load more’ on my Facebook profile page 20 times or more to see anything. Timeline changes that. Now my voting and the public events I attended are very prominent since that’s pretty much the only thing public. And while these were largely very quick responses, these little bits of information suddenly ‘say’ a great deal about me; indeed, for the public, these are the main bits of the story Facebook tells about me.
Now, some of the things I’ve said I’ve attended are pretty trivial, but some are political (it’s very clear what my political views are) and others are on the boundary of personal and political. When I voted ‘Yes’ to ‘Should Same Sex Marriage Be Legal In Australia’ I was stating something publicly, but I’d never considered that my response would be so prominent on Facebook (it wasn’t on my profile page very long, for example). Now, for me, this isn’t a big issue; I’ve got sufficient workplace security that I can’t imagine these views would jeopardise my employment, and I stand by my politics proudly. I suspect, though, this won’t be the case for everyone. I can think of numerous scenarios where this information might be misused by other people and I strongly recommend folks take a look at their Timeline view from the public perspective as soon as it’s available to them.
From what I can see, it is possible to remove certain items from Timeline, or at least reduce their prominence, but you have to do it from your view (not the public view I used to generate the above images) so if you’re a prolific Facebook user, it’ll take a while to find these items and reduce their visibility.
Now, I’m not suggesting Facebook ‘made public’ something that was private. This information may have felt private, but that was based on use, not on a technical sense of security. Indeed, danah boyd expressed this problem in her paper ‘Facebook’s Privacy Trainwreck: Exposure, Invasion, and Social Convergence’ explaining:
The tech world has a tendency to view the concept of ‘private’ as a single bit that is either 0 or 1. Data are either exposed or not. When companies make a decision to make data visible in a more ‘efficient’ manner, it is often startling, prompting users to speak of a disruption of ‘privacy’.
Technically, the information above was always public, but my experience of it meant it felt largely private. My example is extremely banal, but for other people, the sudden prominence of certain information may make it feel a lot more public than they ever intended. While I acknowledge Facebook has started to provide more robust privacy tools, I’ve seen nothing in the hype around Timeline to warn folks about the way their Timeline will tell a different story about them (and a different story to different people – your Friends will see one ‘you’, but the public may see a quite different one). If Facebook is going to be an ongoing repository, the always-being-edited ‘This Is Your Life’, then Facebook and those of us teaching about these tools need to ensure folks have a much better understanding about Timeline and similar changes. When your life story is a series of entries in a database, then the line between public and private is a single setting. However, that database, as we can see, can always be sorted, ordered and presented in very different ways.
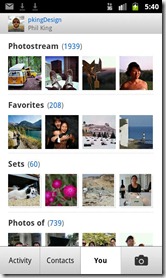
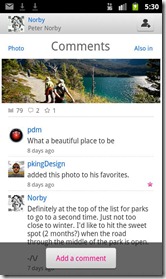
Flickr Android App: It’s all about getting there before Instagram!
Barely rating a mention since it’s not a new tablet (hello Amazon), Flickr relatively quietly launched their official app for Android today. The app itself isn’t bad, pretty seamlessly uploading photos, with a set of basic filters, tagging and some rudimentary tools to engage with your Flickr connections (or ‘friends’ if we were speaking Facebook). However, as the few commentaries have noted, it’s very close to too little, too late. There are a lot of photography-based apps, ranging from Instagram, which is iOS-only for now but clearly the major player there, through to Android equivalents like PicPlz or the ubiquitous photo uploading with Facebook.
Now, don’t get me wrong, I’ve been a huge fan of Flickr for a long time. I’ve been posting my photos to Flickr since September 2004 — there’s more than 3000 on there now — with over half a million views collectively. I’ve also been a paid member “Flickr Pro” for most of that time, and while a few years ago $25/year seemed reasonable for unlimited uploads and the ability to share 90-second HD video, I can only imagine it’s a much tougher sell today (indeed, I suspect most Flickr Pro accounts are maintained by folks like me not wanting to lose their archive rather than any new sign-ups). All of that said, Flickr has summarily failed to embrace mobile devices and tablets. To some extent this has been countered by great APIs which have meant the vast majority of photography apps at least have the option to upload a copy to Flickr. However, it has also meant that Flickr isn’t the destination, it’s the cupboard. Whatever app people have been using, a secondary copy on Flickr means it’s there for the long haul, but the activity has been in the new app ecology, of which Instagram is the exemplar. And I suspect the main reason for the app’s launch now is to try and carve out a space on Android devices before Instagram arrives.
For an application with, lets be fair, a rubbish presence on the web, Instagram has done incredibly well focusing on building their core business: a great photo-sharing app that makes everyone feel like an artful photographer and, more importantly, builds a curational community who love to look at each other’s photos. Instagram is a light-weight app in many ways, but every single feature is the right one; the LIKE button is central, commenting is central, and tagging was lifted wholesale from Twitter and reinforces the seamlessness with which Instagram photos appear in social media streams. And they’ve done so well that within 12 month Instagram have clocked up 10 million users. But Instagram hasn’t arrived on Android yet and none of the various Android-based clones have stood out enough to reign supreme.
For the Flickr Android app, then, the question is how well it compares to Instagram. Now, with the basic filters, tagging, geo-tagging and photo uploading, they are on an even level. Flickr, however, needs to learn very quickly that interacting with photos in a Like Economy means that if you need to open a new menu to Like or Favourite a photo (which you currently do – it’s not on the same initial screen as the photos) then the odds of people liking and sharing pictures is greatly reduced. Flickr also need to radically re-vitalise the community nature of photo-sharing via their app. At the moment, interactions feel cold and forced, compared to the socialability and vibrance of sharing and commenting on Instagram. If Flickr can learn and push out a new version within a few weeks, perhaps they can become the shining light in the Yahoo crown they once were (it’s not like much else in the Yahoo world is getting much attention at the moment).
That said, Flickr does have the advantage of a robust and rich interface on the web. Indeed, I still cherish many of the fine-grain controls offered by Flickr on the web, such as the ability to explicitly chose Creative Commons licenses, and a rich set of tools for grouping and sharing photos in various ways. These tools aren’t widely replicated in apps, and I suspect its the richness of Flickr on the web which might be harnessed to encourage the app users, and build a bridge between the app and the web versions of Flickr. Only time will tell, but I can guarantee if Flickr aren’t monitoring feedback closely and already building a new version of the app, their one shot at establishing themselves in the app ecology will be lost.
Oh, today Flickr also launched “Photo Session” which basically looks like the Hangouts from Google Plus, but based around images, not videos. I can’t imagine Photo Session will find much of a crowd, but we’ll have to see.
You can download the Flickr Android App from the Android Marketplace.