Home » Posts tagged 'visual social media'
Tag Archives: visual social media
Happy birthday Instagram! 5 ways doing it for the ‘gram has changed us
Tama Leaver, Curtin University; Crystal Abidin, Curtin University, and Tim Highfield, University of Sheffield

6 October 2020 marks Instagram’s tenth birthday. Having amassed more than a billion active users worldwide, the app has changed radically in that decade. And it has changed us.
1. Instagram’s evolution
When it was launched on October 6, 2010 by Kevin Systrom and Mike Krieger, Instagram was an iPhone-only app. The user could take photos (and only take photos — the app could not load existing images from the phone’s gallery) within a square frame. These could be shared, with an enhancing filter if desired. Other users could comment or like the images. That was it.
As we chronicle in our book, the platform has grown rapidly and been at the forefront of an increasingly visual social media landscape.
In 2012, Facebook purchased Instagram for a deal worth a $US1 billion (A$1.4 billion), which in retrospect probably seems cheap. Instagram is now one of the most profitable jewels in the Facebook crown.
Instagram has integrated new features over time, but it did not invent all of them.
Instagram Stories, with more than half a billion daily users, was shamelessly borrowed from Snapchat in 2016. It allowed users to post 10-second content bites which disappear after 24 hours. The rivers of casual and intimate content (later integrated into Facebook) are widely considered to have revitalised the app.
Similarly, IGTV is Instagram’s answer to YouTube’s longer-form video. And if the recently-released Reels isn’t a TikTok clone, we’re not sure what else it could be.
Read more: Facebook is merging Messenger and Instagram chat features. It’s for Zuckerberg’s benefit, not yours
2. Under the influencers
Instagram is largely responsible for the rapid professionalisation of the influencer industry. Insiders estimated the influencer industry would grow to US$9.7 billion (A$13.5 billion) in 2020, though COVID-19 has since taken a toll on this as with other sectors.
As early as in 2011, professional lifestyle bloggers throughout Southeast Asia were moving to Instagram, turning it into a brimming marketplace. They sold ad space via post captions and monetised selfies through sponsored products. Such vernacular commerce pre-dates Instagram’s Paid Partnership feature, which launched in late-2017.

The use of images as a primary mode of communication, as opposed to the text-based modes of the blogging era, facilitated an explosion of aspiring influencers. The threshold for turning oneself into an online brand was dramatically lowered.
Instagrammers relied more on photography and their looks — enhanced by filters and editing built into the platform.
Soon, the “extremely professional and polished, the pretty, pristine, and picturesque” started to become boring. Finstagrams (“fake Instagram”) and secondary accounts proliferated and allowed influencers to display behind-the-scenes snippets and authenticity through calculated performances of amateurism.
3. Instabusiness as usual
As influencers commercialised Instagram captions and photos, those who had owned online shops turned hashtag streams into advertorial campaigns. They relied on the labour of followers to publicise their wares and amplify their reach.
Bigger businesses followed suit and so did advice from marketing experts for how best to “optimise” engagement.
In mid-2016, Instagram belatedly launched business accounts and tools, allowing companies easy access to back-end analytics. The introduction of the “swipeable carousel” of story content in early 2017 further expanded commercial opportunities for businesses by multiplying ad space per Instagram post. This year, in the tradition of Instagram corporatising user innovations, it announced Instagram Shops would allow businesses to sell products directly via a digital storefront. Users had previously done this via links.

Read more: Friday essay: Twitter and the way of the hashtag
4. Sharenting
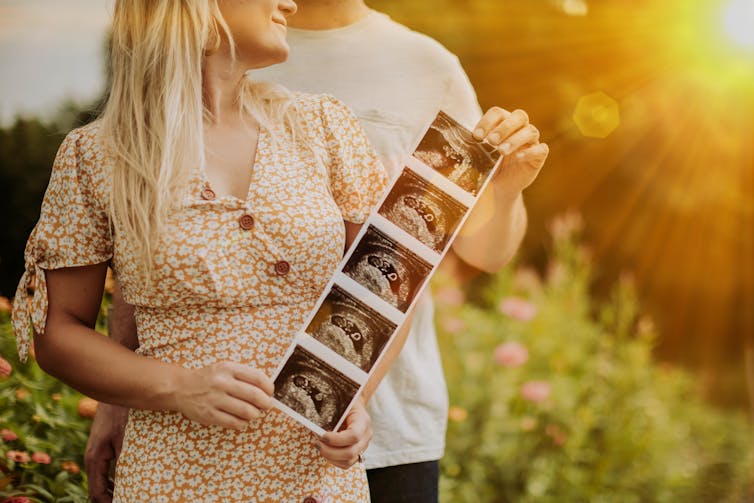
Instagram isn’t just where we tell the visual story of ourselves, but also where we co-create each other’s stories. Nowhere is this more evident than the way parents “sharent”, posting their children’s daily lives and milestones.
Many children’s Instagram presence begins before they are even born. Sharing ultrasound photos has become a standard way to announce a pregnancy. Over 1.5 million public Instagram posts are tagged #genderreveal.
Sharenting raises privacy questions: who owns a child’s image? Can children withdraw publishing permission later?
Sharenting entails handing over children’s data to Facebook as part of the larger realm of surveillance capitalism. A saying that emerged around the same time as Instagram was born still rings true: “When something online is free, you’re not the customer, you’re the product”. We pay for Instagram’s “free” platform with our user data and our children’s data, too, when we share photos of them.

Read more: The real problem with posting about your kids online
5. Seeing through the frame
The apparent “Instagrammability” of a meal, a place, or an experience has seen the rise of numerous visual trends and tropes.
Short-lived Instagram Stories and disappearing Direct Messages add more spaces to express more things without the threat of permanence.
Read more: Friday essay: seeing the news up close, one devastating post at a time
The events of 2020 have shown our ways of seeing on Instagram reveal the possibilities and pitfalls of social media.
In June racial justice activism on #BlackoutTuesday, while extremely popular, also had the effect of swamping the #BlackLivesMatter hashtag with black squares.
Instagram is rife with disinformation and conspiracy theories which hijack the look and feel of authoritive content. The template of popular Instagram content can see familiar aesthetics weaponised to spread misinformation.
Ultimately, the last decade has seen Instagram become one of the main lenses through which we see the world, personally and politically. Users communicate and frame the lives they share with family, friends and the wider world.
Read more: #travelgram: live tourist snaps have turned solo adventures into social occasions
Tama Leaver, Associate Professor in Internet Studies, Curtin University; Crystal Abidin, Senior Research Fellow & ARC DECRA, Internet Studies, Curtin University, Curtin University, and Tim Highfield, Lecturer in Digital Media and Society, University of Sheffield
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Two New ARticles
Two new articles …
 [X] Visualising the Ends of Identity: Pre-Birth and Post-Death on Instagram in Information, Communication and Society by me and Tim Highfield. This is one of the first Ends of Identity article coming from our big Instagram dataset, analysing the first year (2014). We’ll be writing more looking at the three years we collected (14-16) before the Instagram APIs changed and locked us out! Here’s the abstract:
[X] Visualising the Ends of Identity: Pre-Birth and Post-Death on Instagram in Information, Communication and Society by me and Tim Highfield. This is one of the first Ends of Identity article coming from our big Instagram dataset, analysing the first year (2014). We’ll be writing more looking at the three years we collected (14-16) before the Instagram APIs changed and locked us out! Here’s the abstract:
This paper examines two ‘ends’ of identity online – birth and death – through the analytical lens of specific hashtags on the Instagram platform. These ends are examined in tandem in an attempt to surface commonalities in the way that individuals use visual social media when sharing information about other people. A range of emerging norms in digital discourses about birth and death are uncovered, and it is significant that in both cases the individuals being talked about cannot reply for themselves. Issues of agency in representation therefore frame the analysis. After sorting through a number of entry points, images and videos with the #ultrasound and #funeral hashtags were tracked for three months in 2014. Ultrasound images and videos on Instagram revealed a range of communication and representation strategies, most highlighting social experiences and emotional peaks. There are, however, also significant privacy issues as a significant proportion of public accounts share personally identifiable metadata about the mother and unborn child, although these issue are not apparent in relation to funeral images. Unlike other social media platforms, grief on Instagram is found to be more about personal expressions of loss rather than affording spaces of collective commemoration. A range of related practices and themes, such as commerce and humour, were also documented as a part of the spectrum of activity on the Instagram platform. Norms specific to each collection emerged from this analysis, which are then compared to document research about other social media platforms, especially Facebook.
You can read the paper online here, or if the paywall gets in your way there’s a pre-print available via Academia.edu.

[X] Instagrammatics and digital methods: studying visual social media, from selfies and GIFs to memes and emoji in Communication, Research and Practice, also authored by Tim Highfield and me. This paper came out earlier in the year, but I forgot to mention it here. The abstract:
Visual content is a critical component of everyday social media, on platforms explicitly framed around the visual (Instagram and Vine), on those offering a mix of text and images in myriad forms (Facebook, Twitter, and Tumblr), and in apps and profiles where visual presentation and provision of information are important considerations. However, despite being so prominent in forms such as selfies, looping media, infographics, memes, online videos, and more, sociocultural research into the visual as a central component of online communication has lagged behind the analysis of popular, predominantly text-driven social media. This paper underlines the increasing importance of visual elements to digital, social, and mobile media within everyday life, addressing the significant research gap in methods for tracking, analysing, and understanding visual social media as both image-based and intertextual content. In this paper, we build on our previous methodological considerations of Instagram in isolation to examine further questions, challenges, and benefits of studying visual social media more broadly, including methodological and ethical considerations. Our discussion is intended as a rallying cry and provocation for further research into visual (and textual and mixed) social media content, practices, and cultures, mindful of both the specificities of each form, but also, and importantly, the ongoing dialogues and interrelations between them as communication forms.
This paper is free to read online until at least the end of 2016, but if a paywall comes up, there’s a pre-print of this one of Academia.edu, too.
Instagrammatics: Analysing Visual Social Media
At this week’s fantastically engaging CCI Digital Methods Summer School held at Swinburne University in Melbourne, Tim Highfield and I presented a workshop about analysing visual social media, focusing on Instagram data collection and anaylsis. It was based, in part, on our recent First Monday paper, but also looked beyond that at ways of surfacing research questions and approaches. We were pleased with the interest in the workshop, and really positive responses to it, so we’ve shared the slides here:
There will be more on Instagram from us later this year, but if you’re working on Instagram I’d love to hear what you’re doing; either leave a comment here or ping me an email if you want to get in touch.
A Methodology for Mapping Instagram Hashtags
Today First Monday published A Methodology for Mapping Instagram Hashtags by Tim Highfield and myself. This methodology paper explains the processes behind the various media we’ve been tracking as part of the Ends of Identity project, although the utility of the methods go far beyond that. Beyond technical questions, we’ve included some important ethical and privacy questions that arose as we started to explore Instagram mapping. Here’s the abstract:
While social media research has provided detailed cumulative analyses of selected social media platforms and content, especially Twitter, newer platforms, apps, and visual content have been less extensively studied so far. This paper proposes a methodology for studying Instagram activity, building on established methods for Twitter research by initially examining hashtags, as common structural features to both platforms. In doing so, we outline methodological challenges to studying Instagram, especially in comparison to Twitter. Finally, we address critical questions around ethics and privacy for social media users and researchers alike, setting out key considerations for future social media research.
The full paper is available at First Monday, fully open access, with a Creative Commons license. As always, your comments, thoughts and feedback are welcome here, or on Twitter.
